Precision bearings refer to bearings that have reached the precision requirements at the micron level or even the nanometer level through precision machining.
With the continuous progress of technology, the processing requirements for precision bearings are becoming increasingly higher. Especially in industries such as aviation, automobiles and medical equipment, the precision of bearings directly determines the performance and safety of the equipment.
Precision bearings are mainly applied in fields such as aerospace, the automotive industry, medical equipment and high-precision machine tools.
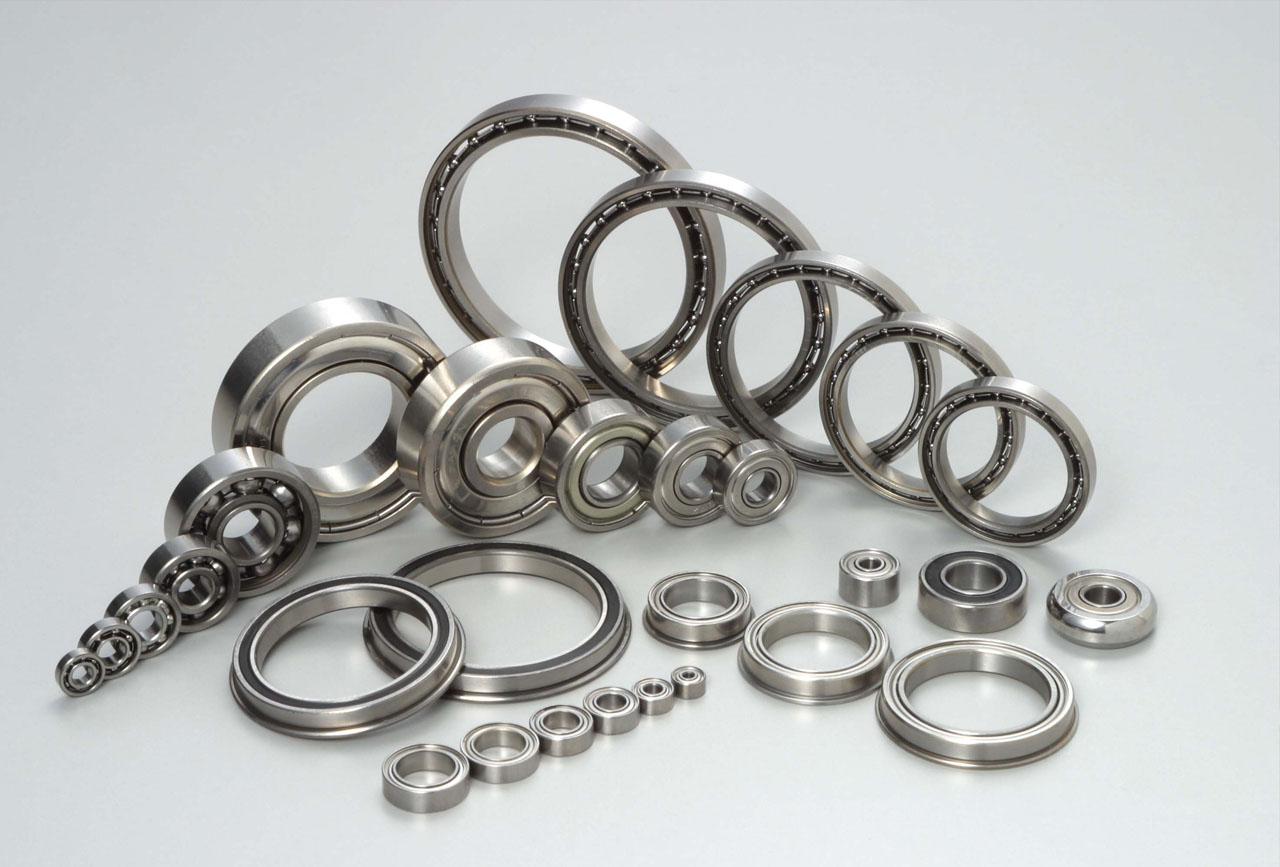
NEWBEE Transmission is a company that specializes in providing precision bearings.Our company has rich experience in the bearing industry for over ten years.We can provide precision bearings of various types, such as thin-section bearings, YRT turntable bearings, slewing bearings, crossed roller bearings, mill bearings and solid oil bearings.Our bearings are mainly exported to many countries at home and abroad, such as those in Europe, North America, Southeast Asia, the Middle East and Africa.

Thin-section four-point-contact ball bearings ( Type X ) are a specialstyle of precision bearing designed for applications where space, weight, and stiffness are critical....
RA Crossed Roller Bearings are a type of roller bearing that are designed to handle high axial,radial, and moment loads simultaneously, making them ideal for applications where precision andstability are critical....
The YRT bearing adopts a design of double-row crossed rollers arranged orthogonally. Through the matching between the precisely ground raceways of the inner and outer rings and the rollers, it provides nanometer-level rotational accuracy. Its compact......
The double row slewing bearing can efficiently bear axial,radial and tilting moment loads through the unique arrangement of two rows of balls. Its robust structure and stable performance make it play a key role in many devices that require high load-......
The Thin Section Angular Contact Ball Bearings(A Type) are mainly applied to support radial and single direction axial loads. ...
Thin-section deep groove ball bearings are a specific type of deep groove ball bearing that features a smaller cross-section and larger bore diameter relative to its thickness....
RB crossed roller bearings are single-row roller bearings that use cylindrical rollers arranged in acrossed configuration. The rollers alternate in direction, which allows them to handle axial, radial, and moment loads simultaneously. ...
RU crossed roller bearing is a high-precision, compact bearing with cylindrical rollers set at 90-degree angles (crisscrossed) within integrated inner and outer rings that often feature mounting holes, allowing it to handle radial, axial, and moment ......
SXU crossed roller bearing is a type of high-precision, compact slewing ring (or turntable bearing) featuring rollers arranged at right angles, designed for supporting heavy radial, axial, and overturning loads with high rigidity, low friction, and e......
CRBH Cross Roller Bearing is a high-precision, compact bearing where cylindrical rollers are arranged in a crossed (90-degree) pattern within separate inner and outer rings, allowing it to handle heavy radial, axial, and moment loads simultaneously, ......
The ZKLDF turntable bearing can efficiently bear radial, axial and overturning moments through double rows of orthogonally arranged cylindrical rollers. Its integrated structure design is especially suitable for CNC equipment that requires ultra high......
The RMWR series working roll bearing is engineered for highspeed rolling mills, offering exceptional precision, durability, and load capacity. Designed to withstand extreme rolling forces (≤6000 kN) and high rotational speeds (≤1500 rpm), it ensures ......
The RMTS series rolling mill thrust bearing is specifically designed to handle extreme axial loads (≤10,000 kN) in rolling mill applications. Engineered for high rigidity, precision alignment, and durability, these bearings ensure smooth operation in......
High-speed wire rod mill bearing employs carburized steel and precision grinding technology, ensuring stable performance under harsh conditions (impact loads, high temperature, dust). Key designs include multi-row symmetric rollers, anti-centrifugal ......
The RMSB rolling mill support bearing features a multi-row cylindrical roller design,specifically engineered for high radial loads (≤8000 kN) and shock loads in extreme steel mill conditions. Its optimized internal structure withstands high temperatu......
The NEWBEE bearing Series cross cylindrical roller slewing bearing is engineered to handle combined axial, radial, and overturning moment loads simultaneously. Its 1:1 cross-arranged rollers and compact structure ensure minimal weight while maintaini......
The Three Row Cylindrical Roller Slewing Bearing achieves independent bearing of axial,radial,and moment loads through the orthogonal arrangement of three rows of cylindrical rollers. Its high-strength structure and optimized load distribution design......
The four-point contact ball slewing bearing features a unique four-point contact design, where steel balls interact with arc-shaped raceways to handle axial, radial, and overturning moment loads simultaneously. Available in split or integral ring str......
Our precision-engineered cages are designed to maximize deep groove ball bearing performance through optimal ball spacing and guidance. These components prevent ball-to-ball contact, reduce friction, and enhance operational stability across speed ran......
Our engineered cages optimize cylindrical roller bearing performance through advanced roller control and load distribution. Designed for demanding industrial applications including machine tool spindles, wind turbines, and heavy equipment, these comp......
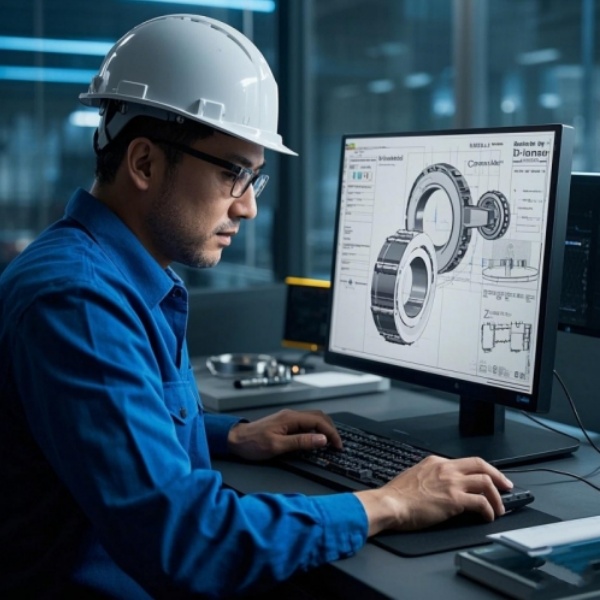

Our company has a professional design team composed of CAD senior engineers, SolidWorks senior engineers and others. According to customers' requirements, we can achieve seamless connection from 2D drawing to 3D model construction and virtual assembly of bearing products.
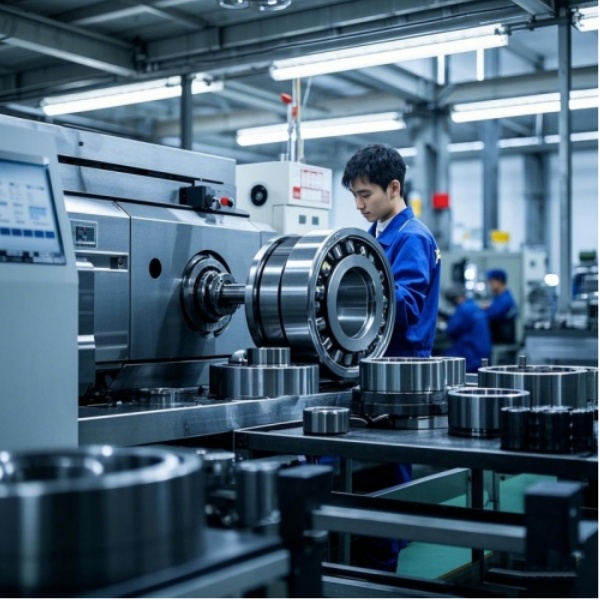
NEWBEE Transmission is a company with modern production workshops. Our company is equipped with professional production equipment such as CNC machining centers, grinding machines, milling machines, external diameter gear grinding machines, CNC drilling machines, quenching machines and dust-free assembly rooms, providing customers with one-stop precision bearing production solutions.
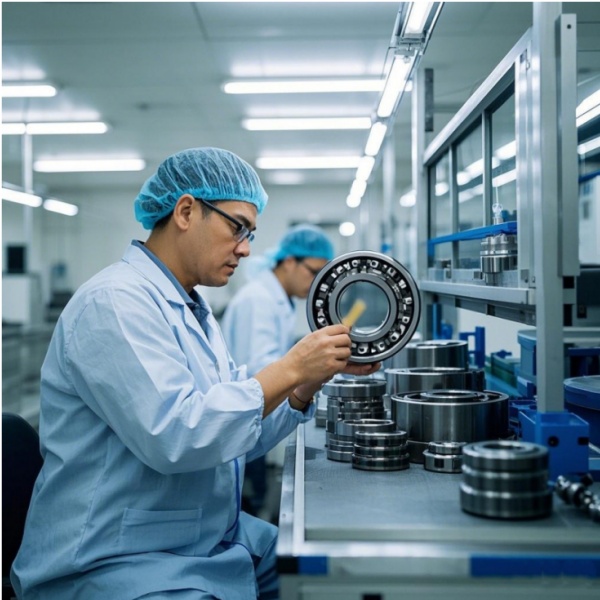


NEWBEE Transmission is a company equipped with a professional inspection system. Our company has professional equipment including roughness profilometers, contact angle measuring instruments, metallographic laboratories, friction torque measuring instruments, roundness measuring instruments. In addition, we have a quality inspection team composed of dozens of members who graduated from colleges and universities and possess professional skills.
Our factory boasts remarkable logistics capabilities. We've partnered with numerous reliable shipping firms for domestic and international deliveries. Our in - house team, well - versed in shipping procedures, ensures seamless operations. With advanced logistics software, we offer real - time order tracking. Plus, our large, well - laid - out warehouse boosts efficiency.

How to customize precision bearings?
1. Requirement Control: Based on your requirements for bearings, including key parameters such as load type, speed range, operating temperature and environment, accuracy class, lifespan requirements, and special needs,we will provide you with professional solutions.
2. Design and R&D: As a core link, we use CAD modeling tools to optimize the internal geometric structure, verify the design reliability through finite element analysis and material mechanics calculations,and select appropriate lubrication schemes to enhance the theoretical performance of the bearings.
3. Production and Manufacturing: According to your requirements for precision bearings, we select suitable materials and conduct appropriate heat treatment.Advanced technologies are applied during the processing to ensure high precision, and the assembly is carried out in a clean workshop to ensure product quality.
4. Quality Inspection: A variety of professional equipment and methods are used to comprehensively inspect the geometric accuracy, dynamic performance, and material quality to ensure that the products meet international standards or specific customer specifications.
5. Delivery Service: We provide high - quality packaging and transportation, offer installation and maintenance guidance, establish a quality traceability system, and conduct failure analysis in a timely manner. We ensure high - quality delivery to meet your performance requirements for high reliability, long lifespan, and extreme working conditions.

In industrial robotics, thin section bearings are crucial for joint parts, offering high precision and flexibility.Their compact design allows for reliable support in limited spaces, bearing radial an...
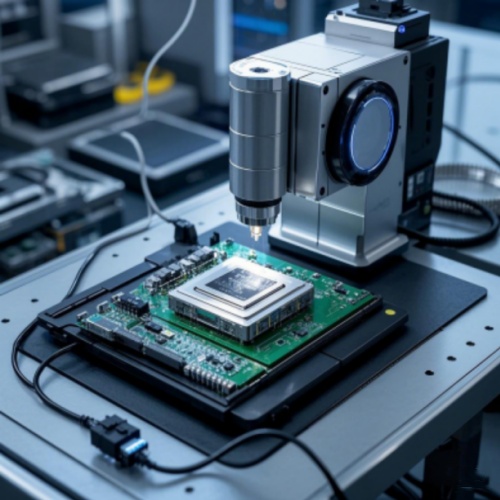
Thin-section bearings play a crucial role in the precision positioning of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, ensuring high-precision patterning. They enable high-speed and stable operation during ...
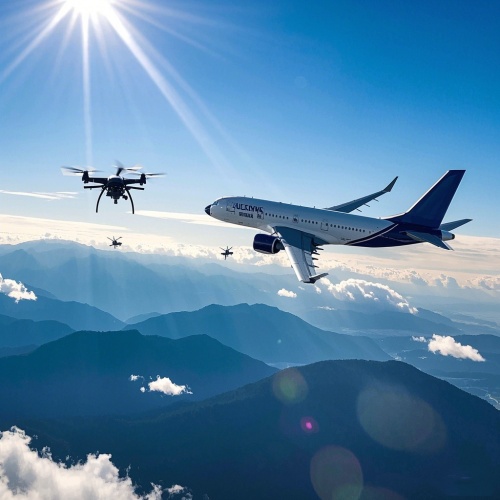

Cross Roller Bearing play a critical role in aircraft landing gear systems, handling high impact forces and ensuring smooth operation during landing, takeoff, and taxiing. In aircraft engines componen...
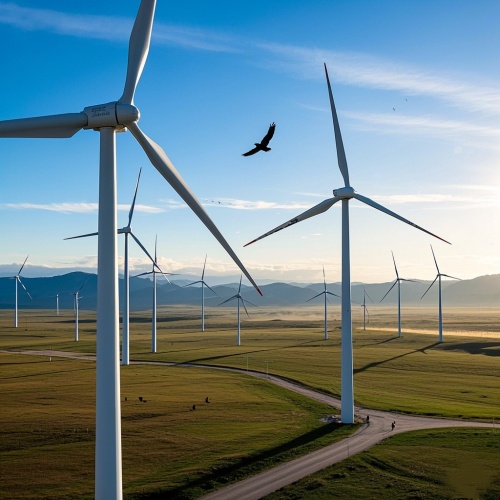

Wind Turbines: In large-scale wind power generating units, slewing bearings are used to support the nacelle and the impeller. They bear various loads under the action of strong winds. Their reliabilit...
What is Precision Bearing?
Precision bearings are specialized rotational components engineered to provide exceptional running accuracy, superior dimensional stability, and precise operational characteristics under demanding conditions. Unlike standard bearings, precision bearings are manufactured to extremely tight tolerances and undergo rigorous quality control processes to ensure consistent performance in critical applications.
These high-precision components are characterized by their exceptional geometric accuracy, minimal runout, and controlled rotational dynamics. The manufacturing process involves advanced grinding techniques, specialized heat treatment, and meticulous assembly procedures to achieve the required precision levels. Precision bearings are typically classified by international tolerance grades such as ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) in the US or ISO standards globally, with grades ranging from ABEC 1 (standard precision) to ABEC 9 (ultra-precision) and beyond for specialized applications.
The fundamental difference between precision bearings and conventional bearings lies in their manufacturing precision, material quality, and performance consistency. While standard bearings may have tolerances measured in hundredths of a millimeter, precision bearings maintain tolerances within microns, making them essential for applications where even minimal deflection or vibration is unacceptable.
The Feature of Precision Bearings
Precision bearings exhibit several distinctive characteristics that make them indispensable in advanced mechanical systems:
Exceptional Accuracy and Low Runout: Precision bearings maintain extremely tight dimensional tolerances, typically within microns. This ensures minimal radial and axial runout, crucial for applications requiring precise positioning and smooth rotation.
High Speed Capability: Designed with optimized internal geometries and premium materials, precision bearings can operate at significantly higher speeds than standard bearings while maintaining stability and generating less heat.
Superior Rigidity: The precise manufacturing and often preloaded design of precision bearings provide high stiffness, reducing deflection under load and maintaining system accuracy during operation.
Low Noise and Vibration: Through careful control of surface finish, geometry, and assembly techniques, precision bearings operate with significantly reduced noise and vibration levels compared to standard bearings.
Enhanced Durability and Life Expectancy: Made from high-grade bearing steel or specialized materials like ceramic, and manufactured with superior processes, precision bearings offer extended service life even under demanding operating conditions.
Thermal Stability: Precision bearings maintain their dimensional accuracy and performance characteristics across a wide temperature range, making them suitable for applications subject to thermal variations.
The Application of Precision Bearings
Precision bearings serve as critical components across numerous high-technology industries:
Machine Tool Industry: In CNC machining centers, lathes, and grinding machines, precision bearings are used in spindles, ball screws, and rotary tables to ensure machining accuracy, surface finish quality, and dimensional consistency of manufactured parts.
Aerospace and Defense: Aircraft control systems, helicopter rotor assemblies, jet engine components, satellite mechanisms, and guidance systems all rely on precision bearings for reliable operation under extreme conditions.
Medical Equipment: High-speed dental handpieces, CT scanner gantries, MRI machines, surgical robots, and laboratory equipment utilize precision bearings for smooth, accurate, and reliable performance where patient safety is paramount.
Robotics and Automation: Industrial robots, collaborative robots (cobots), and automated manufacturing equipment employ precision bearings in joints, actuators, and positioning systems to ensure precise movement and repeatability.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Wafer handling robots, stepper motors, and precision stages in chip manufacturing equipment require the utmost precision and cleanliness provided by specialized precision bearings.
Optical and Instrumentation Systems: Precision bearings enable accurate positioning in telescope mounts, laser scanning systems, measuring instruments, and surveillance equipment where minimal vibration and precise movement are critical.
How to Choose Precision Bearings?
Selecting the appropriate precision bearing requires careful consideration of multiple factors:
Accuracy Requirements: Determine the necessary precision grade based on application requirements. ABEC 3/5 suits most industrial applications, while ABEC 7/9 is reserved for ultra-precision applications like machine tool spindles or medical equipment.
Load Conditions: Analyze the magnitude and direction of loads (radial, axial, or combined). Choose bearing types accordingly – angular contact bearings for combined loads, cylindrical rollers for high radial loads, and thrust bearings for pure axial loads.
Speed Capability: Consider the operational speed range. High-speed applications require bearings with special internal designs, cage materials, and potentially hybrid ceramic construction.
Operating Environment: Evaluate temperature extremes, presence of contaminants, potential corrosion, and lubrication requirements. Special seals, coatings, or materials may be necessary for harsh environments.
Preload and Rigidity Requirements: Determine if preloaded bearing arrangements are needed to eliminate internal clearance and increase system stiffness for applications requiring high positioning accuracy.
Mounting and Installation Considerations: Assess the complexity of installation, available space, and required accessories. Proper installation is critical to maintaining bearing precision and achieving expected service life.
The Price of Precision Bearings
The cost of precision bearings varies significantly based on multiple factors:
Precision Grade: Higher precision grades (ABEC 7/9) command premium prices due to more stringent manufacturing requirements and extensive quality control processes.
Bearing Type and Size: Specialized bearing types like crossed roller bearings, thin-section bearings, or large-diameter bearings are more expensive than standard deep groove ball bearings of comparable size.
Material and Construction: Bearings made from specialty steels, stainless steels, or hybrid ceramics with silicon nitride balls cost significantly more than standard chrome steel versions.
Quantity and Availability: Volume pricing typically applies for larger quantities, while small quantities of specialized bearings carry higher unit costs due to setup and manufacturing overhead.
Brand and Quality: Established manufacturers with proven track records in precision bearing manufacturing typically price their products higher, reflecting their expertise, quality assurance, and technical support.
Additional Features: Special seals, coatings, lubricants, or custom modifications add to the base cost of precision bearings.
As a general guideline, precision bearings can range from 1.5 to 10 times the cost of standard bearings of similar size, with ultra-precision and specialized designs reaching even higher price points.
Precision Bearings Manufacturer
NewBee Transmission has established strategic partnerships with leading precision bearing manufacturers to provide customers with comprehensive bearing solutions. Our technical team possesses extensive experience in bearing selection, application engineering, and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal bearing performance in diverse applications.
When selecting a precision bearing supplier, consider their technical expertise, product range, quality certifications, and after-sales support. A reliable supplier provides not just products but complete solutions, including technical consultation, custom engineering services, and responsive customer support.
At NewBee Transmission, we understand that precision bearings are critical components in your systems. Our commitment extends beyond product delivery to ensuring your success through proper bearing selection, application support, and timely service. Contact our technical team to discuss how our precision bearing solutions can enhance your equipment performance and reliability.
NewBee Machinery provides high quality shaft, bearing, gears, CNC machines and other customized mining machinery.
NewBee Machinery has 20 years’ experience in customize machinery parts.
Professional and effective research and design team
We have advanced large CNC centner and processing equipment.
NewBee Machinery provides cost effective products for global customers.
If you are looking for customized machinery parts, precision bearings or CNC Machinery, feel free to contact us and our team will reply within 48 hours.