A Metric Thin Section Bearing is a compact, lightweight ball bearing with a very small cross-section relative to its bore diameter, designed for space-constrained applications, offering high precision, load capacity, and low friction in standard metric sizes for robotics, medical devices, and aerospace, where reducing weight and saving space are critical.
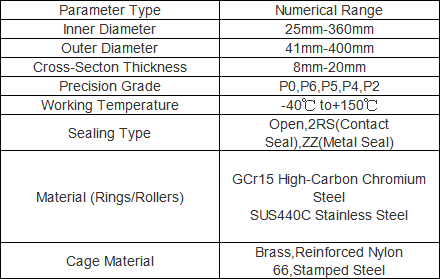
Ultra-thin cross-section design: The radial cross-section (outer diameter - inner diameter) is extremely thin, typically ranging from 3 mm to 20 mm. For example, a bearing with an inner diameter of 50 mm may have an outer diameter of only 56 mm, significantly saving installation space compared to conventional bearings.
Lightweight and compact: Thin-walled structures reduce material usage, making the bearings lightweight (10%-30% lighter than standard bearings of the same inner diameter). This is crucial for equipment requiring weight reduction, such as robotics and aerospace components.
High precision and low friction: Available in precision grades P0, P6, P5, and P4, with radial runout ≤0.005 mm (P5 grade). Precision-ground raceways and rollers (surface roughness Ra≤0.02μm) minimize friction losses, ensuring smooth rotation.
Versatile load-bearing capacity: According to structural types (deep groove, angular contact, four-point contact), they can bear radial loads, axial loads, or combined loads. Four-point contact metric thin section bearings, for example, can withstand bidirectional axial loads, eliminating the need for additional thrust bearings.
Standardized metric sizes: Strictly comply with ISO metric standards, with inner diameters ranging from 10 mm to 500 mm, facilitating interchangeability and compatibility with global equipment designs.
Strong customization adaptability: Supports non-standard metric size customization (e.g., special inner/outer diameter, modified cross-section thickness) and offers multiple sealing (open, 2RS, ZZ) and lubrication (grease, oil) options to meet specific application needs.
Robotics and automation: Used in robotic joints, manipulators, and automated guided vehicle (AGV) wheels. Their compact size and lightweight design adapt to the limited space of robotic arms, ensuring flexible movement and precise positioning.
Aerospace and defense: Applied in aircraft cabin components, UAV frames, and satellite attitude adjustment mechanisms. They meet the requirements of lightweight, high reliability, and extreme environmental resistance in aerospace equipment.
Medical devices: Used in CT scanners, surgical robots, and diagnostic equipment. Their high precision and low vibration ensure the accuracy of medical procedures, while the compact design fits the miniaturization trend of medical devices.
Industrial automation equipment: Applied in linear modules, precision conveyors, and electronic component processing machines. They save space for equipment integration, improving the compactness and efficiency of automation production lines.
Optical and electronic equipment: Used in optical instruments, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and precision sensors. Their high rotational accuracy and low noise avoid interfering with the performance of sensitive electronic components.
Automotive industry: Applied in electric vehicle (EV) drive systems, automotive electronic control units (ECUs), and lightweight vehicle components. They contribute to energy conservation and emission reduction by reducing vehicle weight.
Size and cross-section thickness: Larger inner diameter (e.g., >300 mm) or thicker cross-section (e.g., >15 mm) requires more raw materials and complex processing, increasing costs. Ultra-small metric sizes (inner diameter <20 mm) also have higher production difficulty and higher prices.
Precision grade: P4/P5 high-precision bearings are 30%-60% more expensive than P0/P6 grade bearings due to stricter grinding, testing, and quality control processes.
Material quality: Bearings made of SUS440C stainless steel (corrosion-resistant) or ceramic rollers are 50%-80% more costly than those made of conventional GCr15 steel. High-temperature alloy materials for extreme environments further increase prices.
Structural complexity: Four-point contact or angular contact metric thin section bearings are more expensive than deep groove types due to their sophisticated raceway design and manufacturing processes.
Customization requirements: Non-standard metric size customization, special sealing/lubrication solutions, or surface treatment (e.g., anti-corrosion coating) adds design and production costs, increasing the unit price by 20%-50%.
Order quantity: Bulk orders (≥1000 pieces) enjoy 10%-20% quantity discounts, while small-batch (≤50 pieces) or urgent orders incur additional production scheduling costs.
Operating condition matching: Clarify key parameters such as operating speed (≤3000 rpm for grease lubrication, ≤6000 rpm for oil lubrication), radial/axial load, working temperature (-40°C to +150°C), and environmental conditions (dust, humidity). Select the appropriate structural type (deep groove/angular contact/four-point contact) accordingly.
Size and precision confirmation: Confirm the required metric inner/outer diameter, cross-section thickness, and precision grade based on equipment design drawings. For precision equipment (e.g., surgical robots), prioritize P4/P5 grade bearings; for general automation equipment, P0/P6 grade bearings balance cost and performance.
Material and sealing selection: Choose materials based on the environment (SUS440C for corrosive environments, GCr15 for general conditions) and select sealing types (2RS for dusty environments, open type for high-speed scenarios) to extend service life.
Supplier qualification assessment: Verify the supplier’s production capacity, quality certification (ISO 9001, CE), and after-sales service. Prioritize suppliers with rich experience in metric thin section bearings to avoid quality risks.
Cost-effectiveness balance: Compare prices of different suppliers, but avoid excessive focus on low prices. Consider factors such as product quality, delivery cycle, and technical support to ensure long-term stable operation of equipment.
NEWBEE Transmission (Luoyang New Bee Transmission Co., Ltd.) is a professional supplier of metric thin section bearings, committed to providing high-quality, cost-effective solutions for global customers. With years of experience in bearing R&D and manufacturing, the company has established a complete production and quality control system.
Comprehensive product range: Covers metric thin section bearings of deep groove, angular contact, and four-point contact types, with inner diameters from 10 mm to 500 mm and cross-section thicknesses from 3 mm to 20 mm. Precision grades range from P0 to P4, fully meeting the needs of different industries.
Advanced manufacturing capabilities: Adopts international advanced grinding and testing equipment (e.g., CNC grinding machines, laser interferometers) to ensure product precision and consistency. All products undergo strict fatigue life and performance testing before leaving the factory.
Customization service advantages: Offers non-standard metric size customization, including special inner/outer diameter, cross-section thickness adjustment, and customized sealing/lubrication solutions. Provides one-stop technical support from design to delivery, adapting to personalized equipment requirements.
Reliable quality assurance: Products comply with ISO 9001 quality management system standards and are compatible with international brands such as SKF and NSK. The company provides a 1-year warranty period and efficient after-sales service, including installation guidance and maintenance advice.
Cost-effective supply chain: Localized production and optimized supply chain management enable the company to offer competitive prices, with products 20%-40% more cost-effective than imported brands, realizing high-quality import substitution.
Standardized installation: Use professional tools to avoid bearing damage caused by improper force. Ensure the installation surface is clean, flat, and free of burrs, with fit tolerances controlled within the range of H7/h6 (housing/shaft) to prevent deformation of the thin-walled structure.
Scientific lubrication: Add the appropriate type and amount of lubricant (grease for low-speed, oil for high-speed) before use. Regularly inspect the lubricant condition (contamination, oxidation) and replace it every 3000-5000 operating hours to reduce friction and wear.
Avoid overload operation: Operate within the rated load range. Metric thin section bearings have lower load-bearing capacity than conventional bearings; overload may cause raceway deformation or roller damage. For heavy-load scenarios, select bearings with thicker cross-sections or use multiple bearings in parallel.
Regular operation monitoring: Monitor operating temperature (normal temperature rise ≤20°C), vibration, and noise. Abnormal phenomena such as excessive temperature rise or harsh noise indicate potential issues (e.g., insufficient lubrication, misalignment), requiring immediate shutdown inspection.
Proper storage and handling: Store in a clean, dry, and ventilated environment, avoiding moisture and dust. Place horizontally to prevent deformation of the thin outer ring. During transportation, use shockproof packaging to avoid collision.
Technical Parameters of Metric Thin Section Bearing
For technical specifications, pricing, or custom engineering solutions:
Email: paul@newbeetrans.com
Website: www.newbeetrans.com